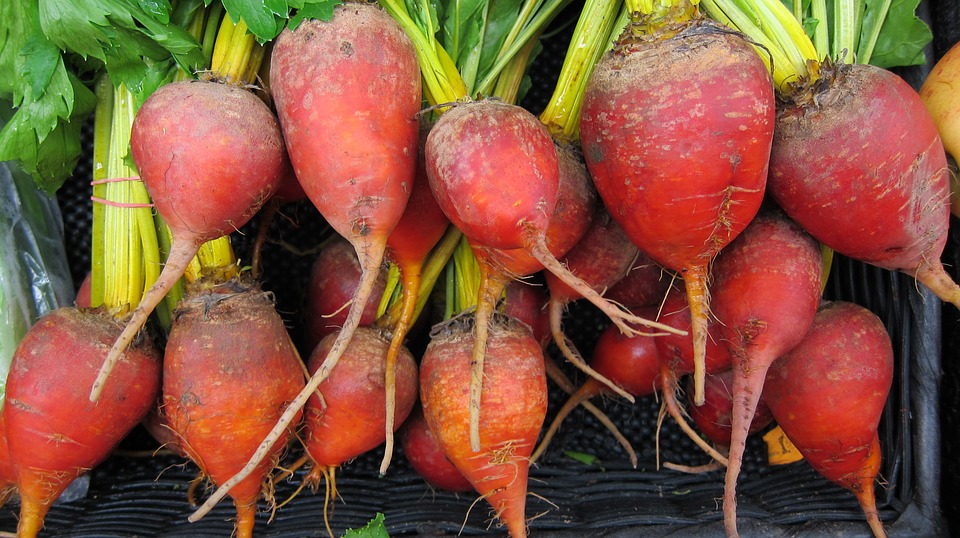
Beetroot juice found to decrease blood pressure and could be a great alternative treatment for people with cardiovascular disease
05/01/2018 / By Isabelle Z.

Cardiovascular disease can be frightening, and it’s understandable that those who have it want to do everything in their power to keep it under control. However, that doesn’t necessarily mean that they need to take on the risks of prescription drugs. A study published in the American Journal of Physiology – Heart and Circulatory Physiology shows that supplementing with dietary nitrate from beetroot juice is a viable alternative.
Those suffering from heart disease often experience an overstimulation of their sympathetic nervous system and an associated higher heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and the constriction of blood vessels. Heart disease encompasses conditions related to narrow or blocked blood vessels such as stroke, heart attack, or angina.
In the study, the researchers looked at 20 people whose average age was 27. In a pair of testing visits, the participants were given either a placebo or a nitrate supplement sourced from beetroot juice. The researchers then measured their heart rate, blood pressure and muscle sympathetic nerve activity. Their muscle activity was measured at rest and then while performing a hand grip exercise using their non-dominant hand. This was measured again after they drank the beetroot juice or the placebo and rested for three hours.
The scientists found that the participants who drank beetroot juice had a lower MSNA burst rate, which indicates nerve activity frequency; their sympathetic nerve activity also dropped when they exercised. There were no blood pressure differences at rest nor during exercise.
The researchers wrote in the study: “These results provide proof-of-concept that dietary nitrate supplementation can modulate central sympathetic outflow and suggest that the established cardiovascular benefits [of dietary nitrate] are likely to involve a neural contribution.”
Beets shown to lower blood pressure
The dietary nitrate found in beets can widen blood vessels, facilitating the flow of blood throughout the body. A study printed in the American Heart Association journal Hypertension showed how potent beet juice can be when it comes to lowering blood pressure, with just 8 ounces of the juice per day lowering people’s blood pressure by a remarkable 10 mm Hg. It’s so powerful that people who are taking hypertension medication could find their blood pressure dipping too low if they use beet juice at the same time.
In addition, beet supplements have been shown to help people who have congestive heart failure to do exercise, which can enhance their quality of life. People whose hearts are not able to pump strongly noted significant improvements in their peak oxygen uptake and exercise duration when they took beetroot supplements while exercising.
Adding beets to your diet
In addition to their heart health benefits, beets have been shown to help prevent the growth of tumors in prostate, breast and pancreatic cancer. It’s also excellent for your eyes thanks to the high amounts of the carotenoid lutein found in beet greens. These can help protect people from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Beets are rich in fiber, which helps digestion, and their low calorie content makes them suited to people who are trying to lose weight. They also have cholesterol-lowering properties and a high amount of alpha-lipoic acid, which can reduce blood sugar and prevent oxidative stress in those with diabetes.
Should you consume more beets? For most people, there are a lot of benefits awaiting. However, those who are susceptible to gout or kidney stones should be cautious as they are high in dietary oxalates. You should also keep in mind that consuming beets or their juice could cause your urine or feces to turn red, which might be mistaken for blood.
Beets are great on sandwiches with vegetables, and they can also be added to green salads or coleslaws. Many people add them to smoothies, and they’re a key ingredient in soups like borscht. There are lots of creative ways to add this nutritious food to the meals you already make so you can gain their natural heart health benefits effortlessly.
Sources for this article include:
Tagged Under: